When it comes to STDs – also known as STIs (Sexually Transmitted Infections) – we want you to be safe. Here’s what you need to know: One may contract these through sexual intercourse – vaginal, oral, anal, or even non-sexual. Simply put, any activity that leads to the intermingling of body fluids can transmit STDs.
STDs can even be transmitted to an unborn foetus during pregnancy and childbirth, but most women who have an STD do not have any health problems in spite of having it.
The main reasons for the rise of STDs mostly revolve around:
- Multiple sexual partners
- Unawareness
There are more than 1 million STDs acquired every day as per the World Health Organization (WHO), affecting both men and women.
The Causes of STDs
STDs are caused by more than 30 different kinds of bacteria, viruses and parasites. 8 out of the 30 are responsible for some of the most common STDs.
Some of the ones that are completely curable if diagnosed and treated early include:
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhoea
- Chlamydia
- Trichomoniasis
The incurable STDs are mostly viral – Hepatitis B, Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV or Herpes), HIV, and Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Their symptoms can be controlled with treatment.
The Symptoms of STDs
The symptoms of an STD can range from none to mild to severe. Some people may develop high fever, foul smelling vaginal discharge, or sudden pain in the tummy. Common symptoms are:
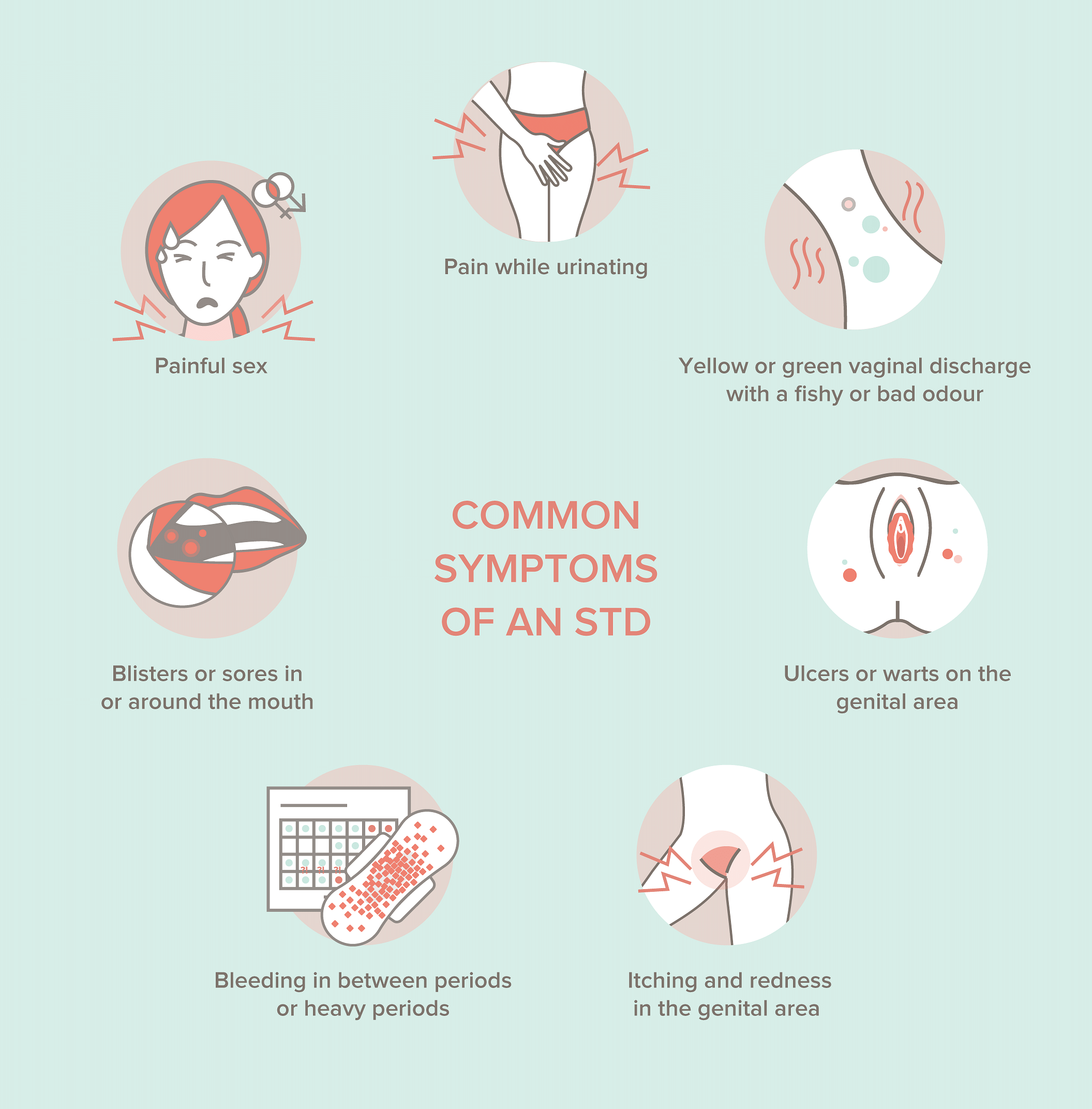
The Implications for Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Not all STDs are curable and may lead to lifelong implications such as:
- Sub fertility or infertility – difficulty to conceive due to tubal damage after Chlamydia
- Tubal ectopic pregnancy – when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus
- Long-term pelvic or abdominal pain
How To Get Tested for STDs
- Gynaecological examination – the nature and odour of vaginal discharge is studied
- Swabs – Vaginal or cervical, penile or genital ulcers
- Blood tests – for diagnosis of viral ones HIV, Hepatitis B or C
STDs Treatment
Like most medical problems, early diagnosis and treatment is essential to limit the damage of an STD. A combination of antibiotics and abstinence (no sex for a while) will go a long way. It’s important to treat current and past sexual partners to prevent reinfection and spread of the infection in the community too.
Prevention is better than cure, and this is 100% true when it comes to the management of STDs. Consider getting yourself vaccinated against STDs like Hepatitis B, HPV, etc. If you are sexually active, always use a condom, even if you are using other methods of contraception. Make sure you and your partners get tested regularly, at least once a year.
Our experts work round the clock to provide you with the answers that you are looking for. So, if you have any, leave it in the comment section below or send us a DM at @nuawoman. This is a safe space that we have built for you so do not hold back on any doubts you may have about your body and mind.
To know more about the intimate parts and how to take care of them, read Dr. Vaishali Joshi’s articles right here. You can also read our other expert content here.






